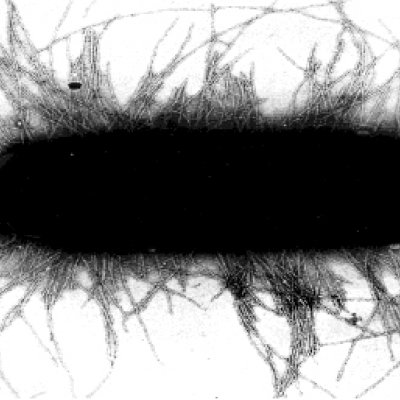
An international study led by The University of Queensland has tracked a potentially devastating multi-drug resistant E. coli strain that is only one gene away from being resistant to almost all antibiotics.
1 April 2014University of Queensland research is investigating if high intensity interval training is an effective treatment to improve health conditions in overweight children and adolescents.
31 March 2014New research from a University of Queensland sociologist shows many doctors over-prescribe antibiotics because they want the best outcomes for individual patients.
28 March 2014University of Queensland researchers have joined forces with hundreds of scientists around the world in a project that is advancing understanding of human genes, giving unprecedented insight into health, development and behaviour.
27 March 2014The Southern Hemisphere's most powerful body scanner, capable of capturing extremely fine anatomical details, is now operating at The University of Queensland.
12 March 2014A pandemic of super-resistant gonorrhoea could be kept in check using new methods to track outbreaks of the disease, according to a University of Queensland infectious diseases expert.
11 March 2014While many students took a well-earned break over summer, Brisbane woman Cindy Bermudez spent her holidays studying plants, bacteria and fungi in an effort to find treatments for infectious diseases.
4 March 2014Researchers have developed a new method for rapidly measuring the level of antibiotic molecules in the blood and how they work against bacteria, paving the way for personalised treatments for bacterial diseases.
3 March 2014- ‹ previous
- 2 of 2